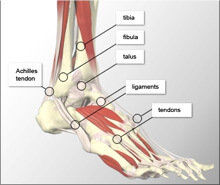
 The ankle is a large joint connecting the foot with the leg. It is made up of three bones called the Tibia, Fibula and Talus and includes three joints called Talocrural, Subtalar and Inferior Tibiofibular. The ankle allows the foot to move in an up and down movement and the Subtalar joint enables the foot to move sideways. Several ligaments are found surrounding the ankle and Subtalar joints. The function of these ligaments is to attach the leg bones to one another and join the ankle bones to the foot bones.
The ankle is a large joint connecting the foot with the leg. It is made up of three bones called the Tibia, Fibula and Talus and includes three joints called Talocrural, Subtalar and Inferior Tibiofibular. The ankle allows the foot to move in an up and down movement and the Subtalar joint enables the foot to move sideways. Several ligaments are found surrounding the ankle and Subtalar joints. The function of these ligaments is to attach the leg bones to one another and join the ankle bones to the foot bones.
Ankle pain refers to any type of pain or discomfort in your ankles. This pain could be caused by an injury, like a sprain, or by a medical condition, such as arthritis.
Ankle pain can be triggered or worsened by injury, activity, over use or ill-fitting shoes. Ankle pain can also be accompanied by, Black-and-blue mark, Burning, Feeling of instability, Flattened arch, Joint deformity, Numbness or tingling, Stiffness or swelling.
Ankle pain is very inconvenient as the ankle is responsible for carrying the whole body weight. Whenever there is pain in the ankle, it is very difficult and sometimes impossible for the patient to even walk normally. Ankle pain can be felt on the inside of the ankle, the outside, or along the tendon that joins the lower leg muscles to the heel bone called “Achilles Tendon”.
The pain felt by the patient could be mild, moderate or severe, depending on the cause of pain. Mild pain can be treated at home with some rest and above the counter pain killers or anti-inflammatory medications. On the other hand, moderate to severe ankle pain may take a lot of time to resolve particularly if an injury was the cause of pain.
Ankle pain can be caused by one or more disorder; these include:
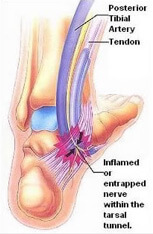 1. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome:This condition occurs when the “Posterior Tibial Nerve” becomes compressed in the tarsal tunnel. This nerve travels at the back of the leg providing the sensory and motor innervations to foot muscles.
1. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome:This condition occurs when the “Posterior Tibial Nerve” becomes compressed in the tarsal tunnel. This nerve travels at the back of the leg providing the sensory and motor innervations to foot muscles.
– The tarsal tunnel is a thin space located on the inside of the ankle next to the ankle bones where the posterior tibial nerve, arteries, veins, tendons and other nerves pass through. When this tunnel becomes narrowed it compresses the posterior tibial nerve, causing a painful condition known as “Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome”.
– This syndrome results in a strong shooting pain in addition to the loss of plantar flexion of the foot and toes. It also causes numbness, tingling and burning sensations as well as weakness in the movement of the foot.
2. Achilles Tendinitis:
This condition occurs when the “Achilles tendon” (which joins the lower leg muscles to the heel bone) is overused causing an injury.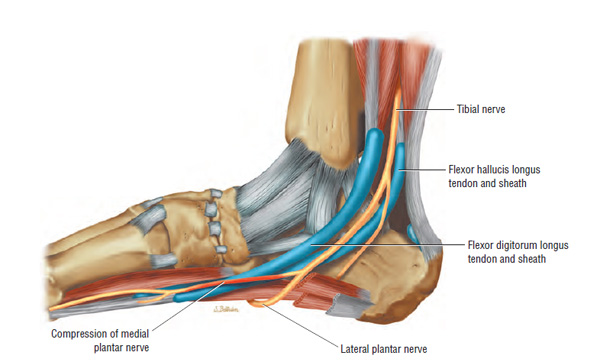
– It most commonly affects individuals who play high impact sports such as running, basketball or tennis where they subject the tendon to extra strain causing it to become inflamed.
– Achilles Tendinitis is often easily treated with home rest, simple pain killers and changing the patient’s exercise routine. With some of the cases, the condition may persist or cause tendon rupture in which case surgery may be required.
3. Ankle Sprain:
When one of the ligaments in the ankle is damaged from an accident such as tripping, falling or twisting or rotating the foot suddenly can cause the ankle to become sprained resulting in pain and swelling and an inability to use the foot normally.
-Sometimes the ligament joining the “Tibia” and “Fibula” lower leg bones can be sprained causing what is known as “High Ankle Sprain” which also causes swelling and pain.
-Ankle sprains require rest and in some cases the use of pain killers and refraining from strenuous foot activities and exercise. In other cases when the condition persists, the patient must consider medical treatment.
4. Ankle Fracture:
A fractured or broken ankle is a condition where one or more of the ankle bones have been broken. These are most commonly those of the lower leg such as the “Tibia” and “Fibula” that usually break due to an accident or a sports injury.
– This condition causes ankle pain and swelling that hinders the patient’s ability to walk or perform daily movements or sports involving the ankle. Breaking one of the ankle bones is generally diagnosed with an x-ray and requires placing a cast on the ankle.
5. Ankle Arthritis:
Ankle Arthritis is a general term for a group of more than 100 diseases. When it affects the ankle joint it can produce swelling and pain, and may eventually result in deformity, loss of joint function, and decreased ability to walk.
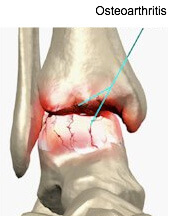 Osteoarthritis is considered a “wear and tear” disease because the cartilage in the joint wears down with repeated stress and use over time. As the cartilage deteriorates and gets thinner, the bones lose their protective covering and eventually may rub together, causing pain and inflammation of the joint.
Osteoarthritis is considered a “wear and tear” disease because the cartilage in the joint wears down with repeated stress and use over time. As the cartilage deteriorates and gets thinner, the bones lose their protective covering and eventually may rub together, causing pain and inflammation of the joint.
Sometimes osteoarthritis develops as a result of abnormal foot mechanics such as flat feet or high arches. A flat foot causes less stability in the ligaments, resulting in excessive strain on the joints, which can cause arthritis.
Similar symptoms may be caused by another form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
– Rheumatoid Arthritis: Patients having this condition are more susceptible to developing ankle arthritis as the rheumatoid causes joint inflammation and cartilage damage. This disease is often associated with pain and a numbing or tingling sensation in the ankle joint.
6. Plantar Fasciitis:
Pain in the plantar fascia is known as “Plantar Fasciitis”, a term used to cover the condition that involves pain and inflammation of the plantar fascia. Symptoms include stabbing pain that usually happens with the first morning steps at the underside of the heel. The pain diminishes with movement, however, long stands or standing up after being seated for a while may trigger an intense pain. The pain may also arise with climbing stairs.
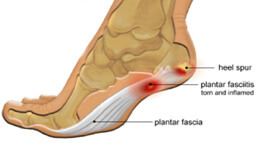
Plantar Fasciitis is a very common condition that is usually caused by increased activities as with runners and especially when running on hard surfaces, overweight, old age and those who wear shoes that do not provide ample foot support. Depending on the cause and extent of pain, sometimes home rest and the use of painkillers can help reduce the pain but if the pain persists medical intervention is required.
7. Tendon sheath inflammation, what is called tendinosis or tendinitis or tenosynovitis:
A tendon is a type of fibrous tissue that connects your muscles to your bones. These tissues help control actions such as running, jumping, grasping, and lifting. Without tendons, you wouldn’t be able to control the movement of your body.
In tendinosis, the synovium ( tendon protective sheath ) gets inflamed and thickened where the more inflammatory fluid is produced, causing pain and discomfort. These tendons are seen around the front, inner side as well as outer side of the ankle. This condition is also sometimes called tenosynovitis.
1. Medication:
– Using anti inflammatory medications which provides varying results from one patient to the other and typically gives short term relief and is ineffective with others.
2. Physiotherapy:
– Performing some physiotherapy exercises with a specialist. This may provide a relief of pain after many sessions. This could be ineffective and some patients do not prefer this type of long course treatment.
3. Pain Killers and Exercise:
– This approach relies on using painkillers combined with stretching exercises and waiting for the pain to improve. This may show an effect within 1 to 6 months.
4. Surgical Intervention:
– When Is Surgery Needed?
When osteoarthritis has progressed substantially or failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be recommended. In advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. The goal of surgery is to decrease pain and improve function.
– Some patients resort to surgery to end the severe pain. This approach has varying results according to the cause and severity of the pain and carries the common risks associated with any surgery or undergoing general anesthesia.
5. Localized pain management injection without image guidance:
– This technique relies on injecting certain medication to the pain area at a doctor’s clinic (not radiologist) to relieve the pain. This approach may result in many complications due to the fact that the doctor can’t see where he injected the medication, so he may inject the wrong spot without any benefit and sometimes-even causes even more pain and discomfort to the patient. Statistic accurate localization of painful spot is about 10-30%.
6. Localized pain management injection with ultrasound guidance (our preferred method of administrating the medication):
– This is a modern, advanced, non surgical treatment technique that relies on injecting specific medication accurately into the area of inflammation under ultrasound guidance. Using an accurate, effective, safe and non invasive technique, make us achieve better results in terms of pain relief/management. Statistic accuracy rate is about 95-99%.
This technique uses FDA approved medication, which is injected, directly into the pain area under ultrasound guidance. This technique has the following benefits:
– Helps the radiologist to accurately identify the inflamed tendon or bursa, which is important to confirm the clinical examination.
– Allows the radiologist to accurately localize and effectively administer the medicine to one or more compartments of the painful area “if necessary” resulting in better and faster pain relief.
– The patient benefits the most by having the medication in the right spot without pain or complications.
– The patient is injected a numbing local anesthetic. A mild burning sensation can be felt due to the numbing anesthetic.
– The radiologist then uses an ultrasound probe to guide the needle to the painful area.
– The medication is then injected in the exact location.
– The injection needle is then removed.
– The patient can leave immediately after the injection. Some patients may be asked to wait for re assessment.
– After the procedure the patient may experience complete relief of pain.
– The maximum effect of the medications may take up to 2 weeks to show the maximum effect.
-The patient is instructed to use painkillers during the first few days if needed.
Different patients respond differently to the same. So one may have a total relief and others may have residual pain and would benefit from another injection.
Most patients report the following after the procedure:
– A great reduction or total elimination of the pain for a period of several weeks after which they may need to have another injection to maintain the results.
– A great reduction or elimination of the pain for several months.
– A great reduction or elimination of pain for years after the procedure especially if complimented with physiotherapy.
Other Treatments

Medication
Using oral or intra muscular anti-inflammatory medications provides varying results from one patient to other, typically giving short-term relief. This may be ineffective with some patients.

Physiotherapy
Performing some physiotherapy exercises with a specialist may relief shoulder pain after many sessions. This may be in effective and difficult with some patient due to the severe shoulder pain, which means that the patient may not be able to perform the recommended exercises.

Pain Killers & Exercise
This approach relies on using painkillers combined with stretching exercises and waiting for the pain to improve. This may show an effect within 1 to 6 months or longer..

Surgical Intervention
Some patients resort to surgery to end the severe pain. This approach has varying results according to the cause and severity of the pain and carries the common risks associated with any surgery or undergoing general anaesthesia.

Comments
Currently have