Below are some of the most frequently asked question on shoulder pain. If you want to ask our team anything specific, please comment in the section below.
What most people call a Shoulder is actually a group of several joints, tendons and muscles that work and combine together to allow free motion of the arm.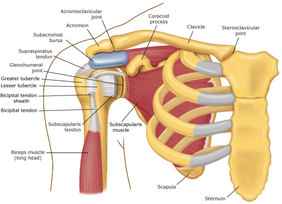
Shoulder pain is one of the most common types of pain that can affect the body. It may originate in the joint itself, or from any of the surrounding muscles, ligaments or tendons. The painful shoulder is usually worse with arm movements, especially when raising the arm to a level above the chest. This aching shoulder can be hindering for the ability to engage in sports or even daily activities. Shoulder pain can be at its worse during the night, where shoulder discomfort can cause many sleepless nights.
Shoulder pain might extend along the front, outer or upper aspect of the shoulder, extending along the outer aspect of the arm and forearm.
Shoulder pain is not specific to a particular age group or sex, but most commonly affects middle age individuals. It also affects sporty individuals as well as elderly population.
Around 3 out of every 10 people suffer from shoulder pain.
The most common causes of shoulder pain are:
1. Tendon inflammation (Tendinosis), Bursitis or Rotator Cuff Tear:
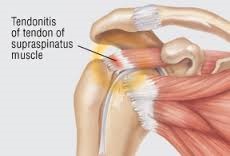
*Tendinosis
A tendon is a cord that connects muscle to its bony attachment and is in continuous use whenever the shoulder is in action. This Most tendinitis is a The continuous action of these tendons results in wear and tear changes within the substance of the tendon and, subsequently inflammation, which lead to thickening of the tendon. This leads to tendon entrapment and rubbing against bones, generating shoulder pain.
Tendenosis can affect any of the rotator cuff tendons, more frequently affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
Generally, Tendinosis is one of two types:
– Acute: can be ferry painful and debilitating if there is associated with calcium deposition. This is called calcific tendinosis.
– Chronic: Occurs due to repeated arm movement above the head. This is seen with jobs, such as decorators and electrician. Swimming or engaging in some types of athletic games is also a well-known cause of aching shoulder. Prolonged, wrong sitting position at work or at home is another precipitation factor.
– Patients who have arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis are susceptible to develop tendon inflammation and impingement.
* Calcific tendinosis:
Its where there is buildup of calcium with the tendon substance, causing hardening and swelling of the tendon and subsequently impingement against the acromion, and eventually pain. The shap of calcium is different than in acute calcific tendinosis.
*Bursitis:
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that are located around tendons and joints throughout the body, including the shoulder. They act as cushions to reduce friction between bones and the overlying soft tissues.
Sometimes, excessive use of the shoulder leads to inflammation and swelling of the subacromial bursa around the shoulder, causing subacromial bursitis, impingement and subsequently pain.
The above can be diagnosed with ultrasound or MRI by a radiology consultant.
2. Frozen Shoulder:
The frozen shoulder condition was named as such because the patient develops a stiff shoulder with restricted movements in all directions. This usually develops after long duration of untreated shoulder pain for what ever the reason.
This above can be diagnosed with clinical examination in addition to ultrasound or MRI .
3. Chronic pain due to chronic advanced shoulder/gleno-humeral joint degeneration:
Shoulder joint (gleno-humeral joint) degeneration as another common cause of shoulder pain. This can be age related or secondary to trauma or chronic joint disease such as Rheumatoid arthritis.
The above can be diagnosed with Plain xray, CT or MRI.
4. Acromioclavicular joint arthritis and inflammation:
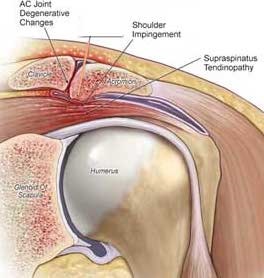
-Due to the frequent daily movements of the shoulder joint and tendons, irritation and injuries may occur within the acromioclavicular joint (known as collarbone joint), causing sever localized pain, tenderness on touching and may also cause localized swelling, especially on moving the shoulder in certain positions.
-The pain occurs at rest and usually worsens when performing sports or carrying heavy weights.
The above can be diagnosed with Plain xray, CT or MRI.
5.Biceps tendinopathy:
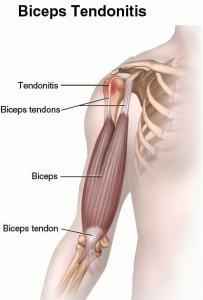
-This is a type of inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon, occurs due to irritation caused by repeated carrying of heavy weight and physical activities.
-If this condition persists, chronic inflammation may lead to complete tendon laceration/tear.
This can be diagnosed by ultrasound or MRI by a consultant radiologist.
6.Cervical nerve roots pressure effect:
Shoulder pain can be referred from the cervical spine as a result of the inflammation and narrowing of cervical neural spaces, compressing nerve roots supplying the arm.
This can be diagnosed by clinical examination and MRI .
7.Trauma/fracture
This can cause severe and long-term pain, but is usually associated with trauma. This is mainly diagnosed with xray.
8. Other reasons for neck and shoulder pain include rheumatoid arthritis affecting the neck and shoulder.
Localized pain management injection with ultrasound guidance (our preferred method of administrating the medication):
This technique uses FDA approved medication, which is injected, directly into the painful area under ultrasound guidance.
This is a modern, advanced, non-surgical treatment technique that relies on injecting anti-inflammatory medication accurately into the area of inflammation under ultrasound guidance. Using an accurate, effective, safe and non-invasive technique, makes musculoskeletal radiologists achieve better results in terms of pain relief/management. Statistic accuracy rate is about 95-99%.
This technique has the following benefits:
-Helps the radiologist to accurately identify the inflamed tendon or bursa, which is important to confirm the clinical examination.
-Allows the radiologist to accurately localize and effectively administer the medicine to one or more compartments of the painful area “if necessary” resulting in better and faster pain relief.
-The patient benefits the most by having the medication in the right spot without pain or complications.
-The patient is injected a numbing local anaesthetic. A mild burning sensation can be felt due to the numbing anaesthetic.
-The radiologist then uses an ultrasound probe to guide the needle to the painful area.
-The medication is then injected in the exact location.
-The injection needle is then removed.
-The patient can leave immediately after the injection. Some patients may be asked to wait for re assessment.
-After the procedure some patients may experience complete relief of pain.
-Some patients may experience pain for 24 hours, until the medication kicks in.
-The patient is instructed to use painkillers during the first few days if needed.
-It is recommended that physiotherapy exercises are followed after 4 weeks of the injection.
Different patients respond differently to the same medication. So one may have a total relief and others may have residual pain and would benefit from another injection (top up).
Most patients report the following after the procedure:
-A great reduction or total elimination of the pain for a period of several weeks after which they may need to have another injection to maintain the results.
-A great reduction or elimination of the pain for several months.
-A great reduction or elimination of pain for years after the procedure especially if complimented with physiotherapy.
Other Treatments

Medication
Using oral or intra muscular anti-inflammatory medications provides varying results from one patient to other, typically giving short-term relief. This may be ineffective with some patients.

Physiotherapy
Performing some physiotherapy exercises with a specialist may relief shoulder pain after many sessions. This may be in effective and difficult with some patient due to the severe shoulder pain, which means that the patient may not be able to perform the recommended exercises.

Pain Killers & Exercise
This approach relies on using painkillers combined with stretching exercises and waiting for the pain to improve. This may show an effect within 1 to 6 months or longer..

Surgical Intervention
Some patients resort to surgery to end the severe pain. This approach has varying results according to the cause and severity of the pain and carries the common risks associated with any surgery or undergoing general anaesthesia.
Due to the frequent daily movements of the shoulder joint, tendon irritation, inflammation, calcification and tears may occur, leading to debilitating shoulder pain.


Comments
Currently have